Introduction
Imagine savouring a light, airy dessert that seems to float on the air but wondering if this delightful treat fits into a diabetic-friendly diet. With its ethereal texture and sweet taste, Angel food cake often tempts those with a sweet tooth. For people with diabetes, every bite comes with a critical question: Will this spike my blood sugar?
With diabetes becoming increasingly common, understanding the impact of favourite foods on health is vital. This isn’t just about resisting temptation; it’s about making informed choices that balance pleasure and well-being. Whether angel food cake is a safe indulgence for people with diabetes touches on broader issues of nutrition, health, and the search for a satisfying dessert that doesn’t compromise dietary needs.
Join us as we delve into this dessert dilemma, uncovering nutritional truths and exploring expert opinions to help you enjoy and eat your cake. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to decide if angel food cake has a place in your diabetic diet or if sweeter, healthier alternatives are waiting to be discovered. Let’s embark on this delicious exploration together and find out if angel food cake is truly an angel in disguise for people with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Dietary Needs
Overview of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body cannot properly regulate blood glucose levels. There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. This type usually develops in children and young adults and requires lifelong insulin therapy for management.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form and typically develops in adults, often associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. In Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, or the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. This type can often be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. However, it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life for both the mother and child.
Diabetes disrupts the normal process where insulin facilitates glucose uptake into cells for energy, leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood, known as hyperglycemia. Chronic hyperglycemia can result in serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Dietary Recommendations for Diabetics
Managing diabetes effectively requires careful attention to diet, particularly the intake of carbohydrates and sugars. Carbohydrates break down into glucose and directly influence blood sugar levels. Therefore, monitoring and controlling carbohydrate intake is essential for people with diabetes. A balanced diet rich in vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is recommended, with controlled portions of fruits and dairy.
The glycemic index (GI) is a crucial tool for diabetics. It ranks carbohydrates from 0 to 100 based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels after eating. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to quick spikes in blood sugar. Conversely, low-GI foods are digested more slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. For example, whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables typically have a low GI, while sugary snacks and processed foods usually have a high GI.
Closely related to the glycemic index is the concept of glycemic load (GL), which considers the quantity of carbohydrates in a portion of food and its GI. Glycemic load provides a more accurate picture of a food’s impact on blood sugar levels. For instance, watermelon has a high GI but a low GL because it contains relatively few carbohydrates per serving. Understanding and utilizing the glycemic index and load can help people with diabetes make informed food choices that minimize blood sugar spikes.
Key strategies include incorporating low-GI foods, practicing portion control, and balancing meals with a mix of macronutrients, including proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. These strategies help maintain stable blood glucose levels and overall health.
Here’s a comparison table of high-GI and low-GI foods:
| Type of Food | Glycemic Index (GI) | Glycemic Load (GL) |
|---|---|---|
| White Bread | High (70+) | High |
| Whole Grain Bread | Low (55 or less) | Low to Moderate |
| Watermelon | High (80+) | Low |
| Lentils | Low (30) | Low |
In summary, diabetes is a complex condition that significantly impacts the body’s ability to manage glucose. Effective dietary management, including monitoring carbohydrate and sugar intake and understanding the glycemic index and load, is crucial for maintaining health and preventing complications associated with diabetes.
What Exactly is Angel Food Cake?

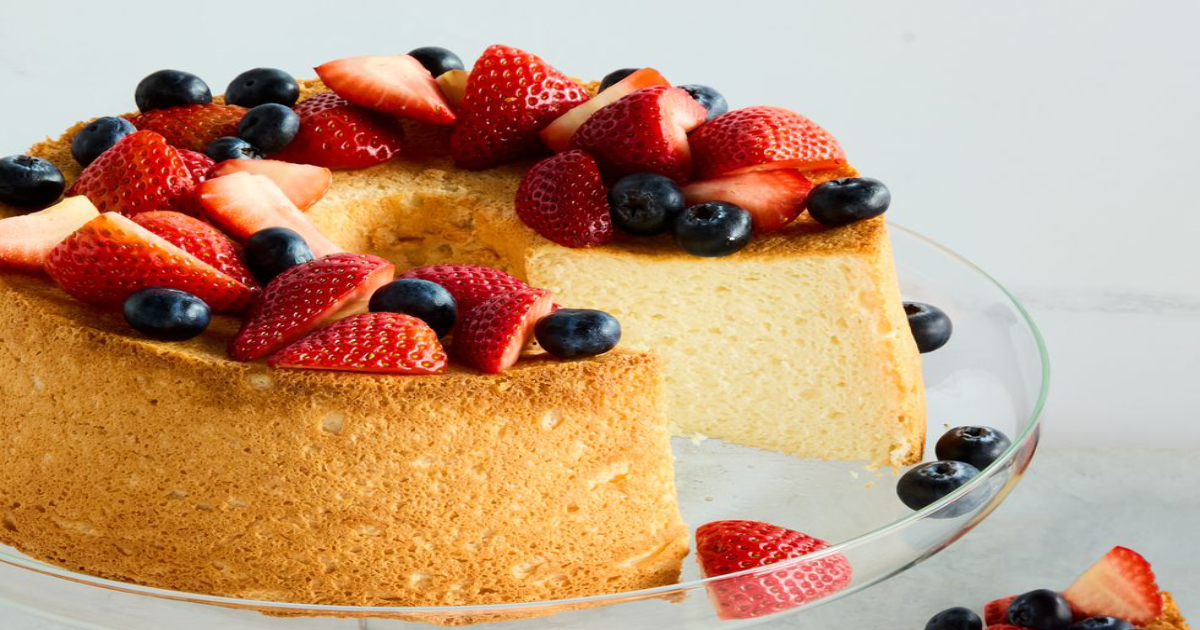
Angel food cake is a sponge cake known for its light and airy texture. It is made from simple ingredients, typically including egg whites, flour, and sugar. The absence of butter or oil in the recipe makes the angel food cake a fat-free dessert option.
The preparation method of angel food cake is unique and essential for achieving its characteristic texture. The process begins with whipping egg whites until they form stiff peaks. This step is crucial because it incorporates significant air into the batter, which is responsible for the cake’s fluffiness. After whipping the egg whites, sugar is added to stabilize the meringue and sweeten the batter. The flour is then gently folded to ensure the mixture retains its airy consistency. The batter is poured into an ungreased tube pan, which allows the cake to rise properly. Once baked until golden brown, the cake is typically cooled upside down to prevent it from collapsing and help maintain its structure. This careful handling ensures the cake remains light and airy.
Angel Food Cake vs. Other Cakes
Several differences stand out when comparing angel food cake to other famous cakes, such as chocolate cake or cheesecake. Chocolate cake usually contains butter or oil, eggs, sugar, flour, and cocoa powder, making it denser and higher in fat and calories. Cheesecake is richer, made with cream cheese, sugar, eggs, and a graham cracker crust, resulting in a dessert high in fat, calories, and often sugar. These differences highlight why some might consider angel food cake a lighter option.
To address the question, “Is angel food cake healthier than other cakes?” we can look at its nutritional profile. Angel food cake is lower in fat and calories than many other cakes, making it a potentially better choice for those watching their weight or reducing their fat intake. However, it’s important to note that while angel food cake is lower in fat, it is still high in sugar, which can be a concern for individuals with diabetes or those managing their blood sugar levels. Therefore, moderation is key.
Here’s a comparison table of angel food cakes and other common cakes:
| Cake Type | Calories per Serving | Fat Content per Serving | Sugar Content per Serving |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angel Food Cake | 140-160 | 0 grams | 20-25 grams |
| Chocolate Cake | 350-450 | 15-25 grams | 35-45 grams |
| Cheesecake | 400-500 | 20-30 grams | 30-40 grams |
Overall, angel food cake offers a lower-fat, lower-calorie alternative to denser, more decadent cakes. However, its high sugar content means it should still be consumed in moderation, especially by those with dietary restrictions related to sugar intake. By understanding its composition and preparation, individuals can make informed decisions about including angel food cake in their diet.
Sure! Here is a sentence with the internal link:
If you’re wondering can diabetics eat angel food cake, our guide provides comprehensive insights into managing sugar intake while enjoying desserts.
Nutritional Analysis of Angel Food Cake
Understanding the nutritional content of angel food cake is crucial for determining its suitability in a diabetic diet. The two primary dietary components of concern are carbohydrates and sugars, the overall caloric content and nutritional value.
Carbohydrates and Sugars
A standard serving of angel food cake, typically about 1/12th of a whole cake, contains approximately 30 to 35 grams of carbohydrates. Of these carbohydrates, around 20 to 25 grams are sugars. This high sugar content is significant, especially for individuals with diabetes who need to manage their blood sugar levels carefully.
To provide a clearer picture, here’s a breakdown of the carbohydrate and sugar content per serving:
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving (1 slice, 1/12th of cake) |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 30-35 grams |
| Sugars | 20-25 grams |
Given this information, “Is angel food cake high in sugar?” is answered affirmatively. Despite being lower in fat, angel food cake has a considerable amount of sugar, which can cause spikes in blood glucose levels if consumed in large quantities or without appropriate balance in the diet.
Caloric Content and Nutritional Value
In addition to carbohydrates and sugars, the caloric content of angel food cake is another essential factor to consider. A typical slice contains between 140 and 160 calories. While this is relatively low compared to richer desserts like chocolate cake or cheesecake, it is important to note that these calories are primarily derived from sugars.
Here’s a comparison table of the caloric content of angel food cake and other popular desserts:
| Dessert | Calories per Serving |
|---|---|
| Angel Food Cake | 140-160 |
| Chocolate Cake | 350-450 |
| Cheesecake | 400-500 |
Angel food cake’s lower calorie count can benefit those who manage their weight. However, its high sugar content
This can offset these benefits, particularly for people with diabetes who need to control their blood sugar levels.
While angel food cake provides some protein from egg whites, it lacks other essential nutrients, including fibre, vitamins, and minerals crucial for overall health. The absence of fibre is particularly notable since fibre helps slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, aiding in blood sugar management.
In summary, while angel food cake is lower in calories and fat than many other desserts, its high sugar content and lack of essential nutrients mean it should be consumed in moderation, especially for those managing diabetes. Balancing its consumption with fibre-rich foods and maintaining overall portion control can help mitigate its impact on blood sugar levels.
Angel Food Cake in a Diabetic Diet
Angel food cake can be a delightful and relatively healthier dessert option for individuals managing diabetes, thanks to its lower carbohydrate content compared to many traditional cakes. Made primarily from egg whites, sugar, and flour, angel food cake has a light and airy texture that satisfies sweet cravings without the excessive calories and fat found in other desserts. By using sugar substitutes and incorporating whole grain flours, the glycemic impact can be further reduced, making it an even more suitable treat for those with diabetes. Enjoying angel food cake in moderation, paired with fresh fruits or a light whipped topping, can offer a satisfying dessert experience while keeping blood sugar levels in check.

Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Angel food cake’s impact on blood sugar levels can be understood through its glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL). The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, while low-GI foods result in a slower, more gradual increase.
Angel food cake has a medium GI, which causes a moderate rise in blood sugar levels. This is significant for people with diabetes who must manage their blood glucose levels carefully. The glycemic load provides a more accurate picture of a food’s impact on blood sugar as it considers both the GI and the amount of carbohydrates in a serving. With its high carbohydrate and sugar content, Angel food cake has a moderate to high GL, making it essential for people with diabetes to consume it in controlled portions.
Pros and Cons for Diabetics
Consuming angel food cake for diabetics has advantages and disadvantages. One of the primary benefits is its low-fat content. Unlike many other cakes, angel food cake is made without butter or oil, making it a lower-fat option, which can be beneficial for those managing weight and heart health.
However, the high sugar content poses a significant risk. A typical serving of angel food cake contains 20 to 25 grams of sugar, which can lead to spikes in blood glucose levels, which is particularly dangerous for people with diabetes. Balancing the pros and cons involves careful consideration.
Here’s a summary table:
| Factor | Angel Food Cake |
|---|---|
| Glycemic Index | Medium |
| Glycemic Load | Moderate to High |
| Fat Content | Low |
| Sugar Content | High |
| Caloric Content | Lower than many desserts |
The low-fat and calorie content can make angel food cake appealing, but the high sugar content requires careful portion control and moderation. For people with diabetes, it is essential to pair angel food cake with fibre-rich foods to help slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Additionally, consuming it as part of a balanced meal with proteins and healthy fats can mitigate some of the potential spikes in blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, while angel food cake offers some benefits due to its low fat, high sugar, and moderate to high glycemic load, it necessitates cautious consumption by people with diabetes. By understanding these factors and balancing their diet accordingly, people with diabetes can enjoy angel food cake in moderation without severely impacting their blood glucose levels.
Making Healthier Choices: Diabetic-Friendly Desserts
When managing diabetes, making healthier dessert choices is crucial to maintaining stable blood sugar levels without sacrificing the joy of sweet treats. Diabetic-friendly desserts can be both delicious and nutritious by incorporating ingredients that are low in sugar and high in fiber. Substituting refined sugars with natural sweeteners like stevia, erythritol, or monk fruit can significantly reduce the glycemic load. Additionally, using whole grain flours, almond flour, or coconut flour instead of refined flour adds nutritional value and fiber, helping to slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Fresh fruits, yogurt, and nuts can also be creatively used to add flavor, texture, and essential nutrients to desserts. By experimenting with these healthier alternatives, individuals with diabetes can enjoy a wide variety of satisfying and safe desserts.
Alternatives to Angel Food Cake
When considering alternatives to angel food cake, it is essential to focus on cakes that are low in sugar and high in fibre. Cakes made with almond flour or coconut flour are excellent options. These flours have a lower carbohydrate content than traditional wheat flour and are rich in fibre, which helps manage blood sugar levels.
For example, almond flour is a popular choice for diabetic-friendly baking. It has a low glycemic index and is high in protein and healthy fats. Coconut flour is another great alternative; it is high in fibre and absorbs more liquid, which can help create moist, delicious cakes with fewer carbohydrates. Incorporating fruits like berries into desserts can also enhance their nutritional value. Berries are low in sugar and high in antioxidants and fibre, adding natural sweetness and flavour to cakes without refined sugars.
Here’s a comparison of some diabetic-friendly flour options:
| Flour Type | Carbohydrate Content (per cup) | Fiber Content (per cup) |
|---|---|---|
| Almond Flour | 24 grams | 12 grams |
| Coconut Flour | 16 grams | 10 grams |
| Wheat Flour | 95 grams | 3.4 grams |
Modifying Angel Food Cake for Better Health
Modifying the traditional angel food cake recipe can make it more suitable for a diabetic diet. One way to reduce sugar content is to use alternative sweeteners. Stevia and erythritol are popular because they provide sweetness without raising blood sugar levels.
For example, replacing regular sugar with a stevia blend can significantly reduce carbohydrate content. Erythritol, a sugar alcohol, is another excellent substitute that does not impact blood glucose levels. These sweeteners can be used in the same quantity as sugar, making them convenient for recipe adjustments. Another modification is to incorporate whole grain or alternative flours into the batter. Adding a small amount of almond or oat flour can increase the fibre content, helping slow down sugar absorption. This can be particularly beneficial for people with diabetes as it helps maintain more stable blood glucose levels.
Here’s a sample modification to a traditional angel food cake recipe:
| Ingredient | Traditional Recipe | Modified Recipe |
|---|---|---|
| Sugar | 1 cup | 1 cup stevia blend |
| All-purpose Flour | 1 cup | 1/2 cup almond flour + 1/2 cup all-purpose flour |
By making these adjustments, the modified recipe maintains the angel food cake’s light, airy texture while being more suitable for a diabetic diet. These changes can help reduce the glycemic load and make the dessert healthier overall.
In summary, choosing alternatives like almond or coconut flour and incorporating natural sweeteners can make desserts more diabetic-friendly. Modifying traditional recipes, such as angel food cake, by reducing sugar and increasing fibre content can create healthier options. These strategies allow people with diabetes to enjoy sweet treats without significantly impacting their blood glucose levels.
Expert Opinions and Studies
Nutritionist Insights
Nutritionists often emphasize balance and moderation when consuming desserts with diabetes. Registered dietitian Jessica Cording explains that enjoying sweets in moderation can be part of a healthy diet. She advises, “It’s important to focus on portion control and pairing sweets with other foods with protein and fibre to help stabilize blood sugar levels.”
Another expert, dietitian Lori Zanini, recommends being mindful of ingredients. She states, “Opt for desserts made with whole grains and natural sweeteners, as these can have a less dramatic impact on blood sugar levels.” This advice aligns with modifying traditional dessert recipes to be more diabetic-friendly.
Nutritionist Joey Bauer adds that it’s crucial to listen to your body. She says, “If you notice that certain sweets cause significant blood sugar spikes, it’s best to limit those and find alternatives that your body can handle better.”
Recent Research
Recent studies have explored the impact of desserts on blood sugar levels, offering valuable insights for people with diabetes. One study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition examined the effects of different types of carbohydrates on blood sugar control. The study found that low-glycemic index foods, including certain types of desserts, led to better blood sugar management.
Another study conducted by the Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice journal focused on sugar substitutes. Researchers found that alternative sweeteners like stevia and erythritol can help reduce blood sugar spikes without compromising taste. This supports the idea that modified recipes can be enjoyable and healthier for people with diabetes.
A comparative study in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism analyzed traditional desserts versus modified, lower-sugar versions. The results showed that participants who consumed the modified desserts had significantly lower postprandial blood glucose levels. This highlights the potential benefits of making simple recipe changes.
Here’s a summary table of some key findings from recent studies:
| Study | Key Finding |
|---|---|
| American Journal of Clinical Nutrition | Low-GI foods improve blood sugar control |
| Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice | Alternative sweeteners reduce blood sugar spikes |
| Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism | Modified desserts lead to lower postprandial glucose levels |
In summary, nutritionist insights and recent research underline the importance of moderation and thoughtful ingredient choices for people with diabetes. By following expert advice and considering scientific findings, individuals with diabetes can enjoy desserts like angel food cake without significantly impacting their blood sugar levels. Balancing these treats with a healthy diet and monitoring blood glucose responses are essential strategies for managing diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, angel food cake offers certain benefits, such as low fat and calorie content, but its high sugar content makes it less ideal for people with diabetes. Careful portion control and occasional indulgence can help manage its impact on blood sugar levels. People with diabetes are encouraged to consult healthcare providers to tailor their diets to their specific needs.
FAQs
1. What kind of cake is suitable for people with diabetes?
Cakes with low sugar and high fibre content, such as those made with almond or coconut flour, are better for people with diabetes.
2. Is Angel Food Cake high in sugar?
Yes, angel food cake contains significant amounts of sugar, which can impact blood sugar levels.
3. Is Angel Food Cake healthier than other types of cake?
While it is lower in fat and calories, its high sugar content can still pose challenges for people with diabetes.
4. Is Angel Food Cake low glycemic?
No, angel food cake has a moderately high glycemic index, which can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
5. Can people with diabetes eat angel food cake without health risks?
With careful portion control and occasional indulgence, people with diabetes can enjoy angel food cake. However, monitoring blood sugar levels and consulting healthcare providers is important.